

Notícias
Rail-mounted container gantry cranes (RMGs) and rubber tyre-mounted container gantry cranes (RTGs) are widely used in modern ports and logistic hubs for efficient container loading, unloading, and transshipment. RTG vs RMG cranes have their advantages, this article will analyze them in depth from the structural differences, working principles, and performance parameters, to help you make the right choice according to your actual needs. Please continue reading this article.
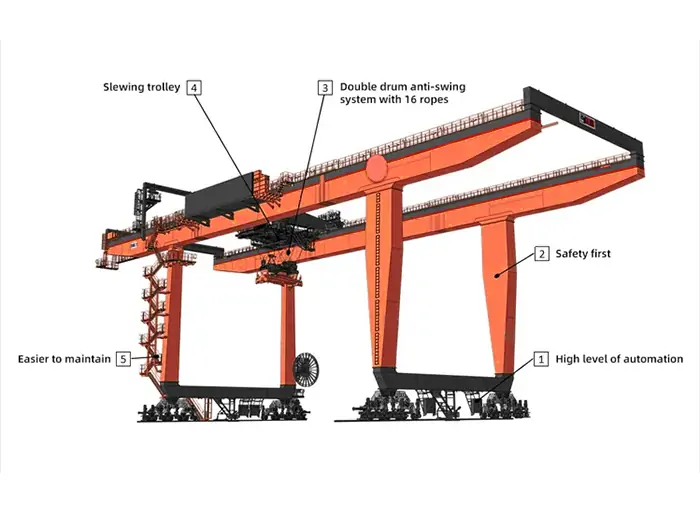
RMG and RTG are significantly different in overall structure and appearance design. The following are the differences in the functions of the main components:
RMG rail-mounted cranes use a steel wheel support system and run on a fixed track, usually consisting of 16-24 steel wheels.RMG has very high stability and load carrying capacity, but mobility and flexibility are limited, and they can only be stacked in a limited space, and cannot be used for inter-yard transfer operations. RTG tire cranes, on the other hand, rely on the support of multiple heavy-duty rubber tires, have excellent maneuverability and a variety of steering modes, and can be flexibly transferred between container yards.
RMGs usually use a three-phase AC 380V/50Hz power supply directly and transmit power through the skid line or cable reel system, which is pollution-free, has low energy consumption, and can provide more stable power output. The traditional RTG mostly uses diesel generator sets as the power source (three drive modes are available: diesel-electric or diesel-hydraulic drive), which is more flexible to move, but produces noise and exhaust emission problems. In recent years, the new RTG can be driven by electric power through cable reels, low-altitude skidding lines, or overhead skidding lines, etc., which effectively reduces operating costs and environmental impact.
Both rail-mounted container gantry cranes (RMG) and rubber tire-mounted container gantry cranes (RTG) contain a hoisting mechanism, a trolley running mechanism, trolley running mechanism and a spreader system, but they differ in specific configurations. The hoisting mechanism of RMG generally adopts a single-reel design (it can also be customized as a double-reel) and is equipped with AC variable frequency motors, and the lifting speed is usually faster than that of RTG. The RTG's hoisting mechanism mostly uses constant power vector closed-loop control, which helps reduce motor power requirements. In terms of anti-shaking systems, RMG is usually equipped with a two-way flexible resistance anti-shaking system as standard, and can be equipped with an optional electronic anti-shaking system, which has a better anti-shaking effect than traditional RTG.
Both adopt a box girder structure, but RMG can be designed with larger spans and cantilevers (single cantilever, double cantilever, and no cantilever configurations) to adapt to different container yard layouts. RTGs usually have relatively small spans and are usually not equipped with cantilevers. Modern RMG mostly adopts a modularized design, which allows multiple machines to carry out synchronous joint operation and improve the efficiency of yard operation.
Safety system, both types of equipment are equipped with a comprehensive multi-protection mechanism. RMG integrates more powerful safety features, such as high wind warning systems, dynamic safety scanning, and STO/SS1/SLS/SBC, etc., to ensure safety under high-speed operation. RTG has anti-roll-over protection and tire pressure monitoring, and some models are also equipped with a GPS positioning system, which is convenient for fleet management and dispatching. Both devices comply with international and domestic safety standards such as FEM, DIN, IEC, AWS, GB, etc. to ensure the safety of operators and equipment.
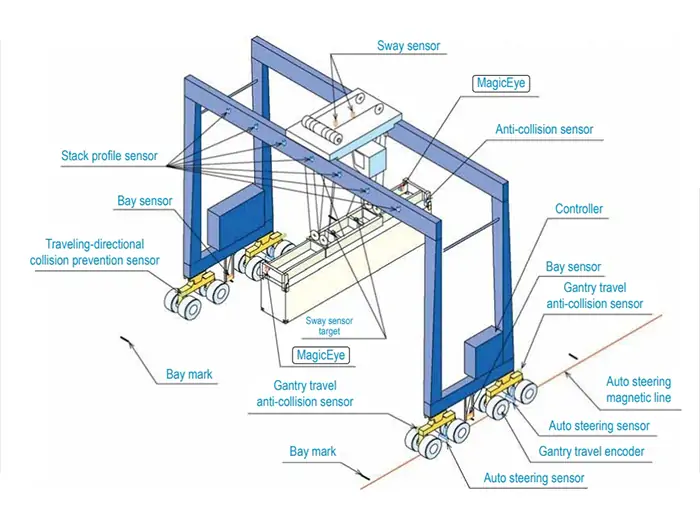
RMG rail-mounted cranes are based on fixed rail operation and adopt a steel wheel traveling system with high positioning accuracy, and are equipped with a bi-directional flexible anti-rocking system as standard, which works with laser positioning to achieve stable operation.RMG supports fully automated operation and seamlessly integrates with the yard management system through the PLC control system.

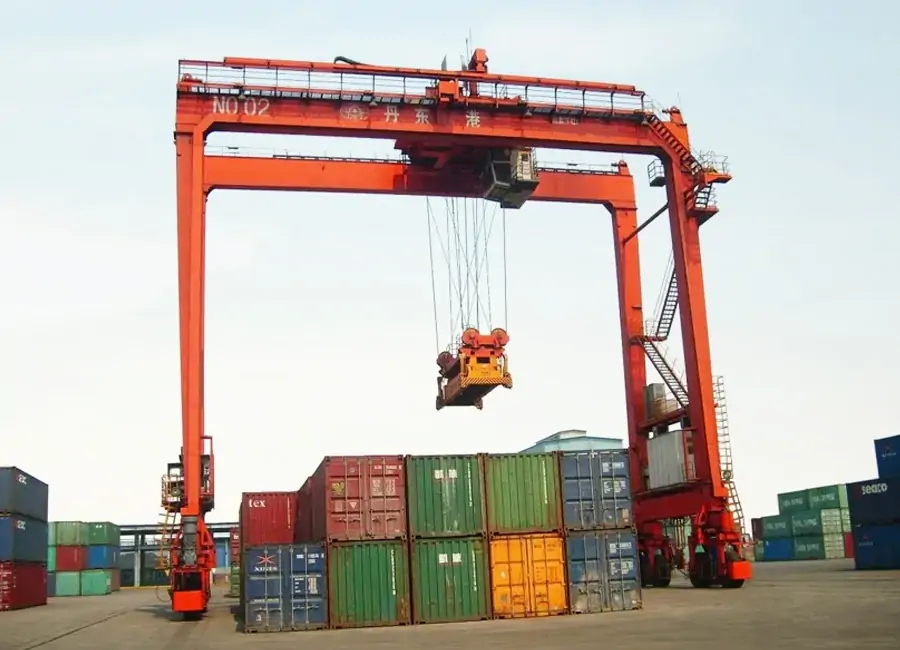
RTG tire cranes rely on rubber tires to move freely between different yards. Through the specialized steering mechanism (can realize 0-90 degrees in-situ steering) to adjust the running direction, with straight, traverse, and diagonal ability, with mobility and flexibility, but need to be equipped with a large vehicle deflection correction system to maintain straight operation, positioning accuracy is lower compared with RMG. The traditional RTG is mainly operated by cab, while the new RTG supports remote control and semi-automatic modes.

In terms of control mode, both devices support multiple operation modes: RMG usually provides manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic modes, and in automated yards, it can be directly dispatched through the upper control system to realize the cooperative operation with other devices, such as AGVs etc. Due to its flexible and mobile characteristics, RTG needs to be operated by the driver, and at present, the new automated RTGs are equipped with three types of operation modes, including local cab operation, ground remote control operation, and remote centralized operation. Currently, the new automated RTG is equipped with three operation modes, including local cab operation, ground remote control operation, and remote control room operation, which greatly improves the operation flexibility.
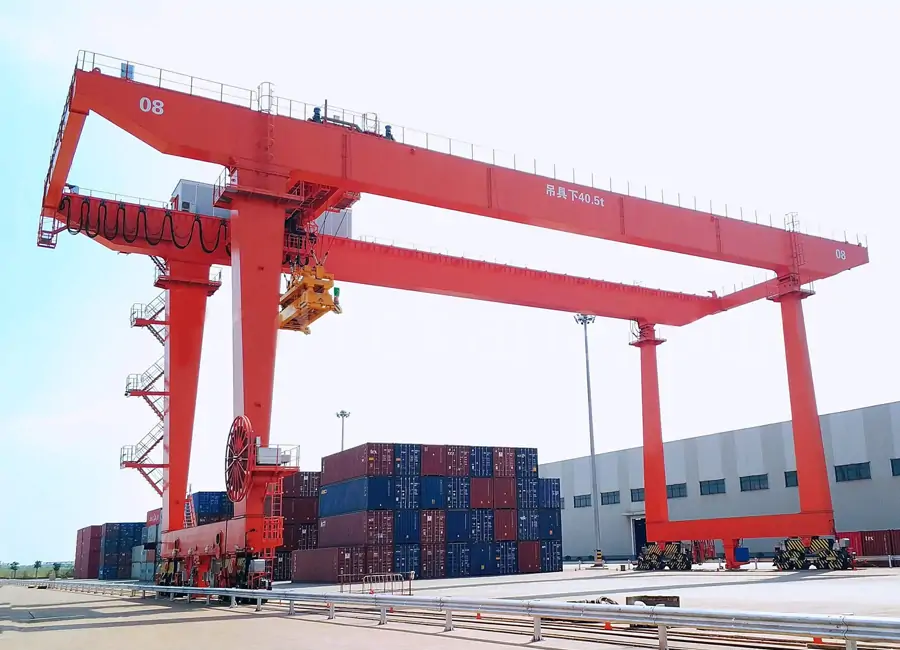
With high stability, large span, and excellent automation compatibility, RMG rail cranes are capable of high-density stacking of 5 or even 6 layers of containers, which are especially suitable for large container terminals for high-intensity and high-efficiency long-term stationary operation scenarios. Its single or double cantilever design can effectively cover a wider working area.RMG is widely used in railroad yards, seamlessly connecting with railroad flatcars, efficiently completing the transfer operation of containers between railroad and road transportation modes.RMG is often used in terminals with a high degree of automation, and systematic synergistic operation with AGVs, automated guided vehicles, and other equipment, realizing the unmanned operation of the whole yard process.
In contrast, RTG tire cranes are flexible and adaptable, capable of stacking containers 4-5 layers, and can be easily transferred between different yards, which is especially suitable for scenarios such as multi-purpose terminals, small and medium-sized ports, and inland logistics parks. Commonly used in highway transfer stations, it operates over semi-trailers without the need for complex docking systems. Moreover, diesel-powered RTGs can be used in areas with poor electrical infrastructure or temporary operating sites, while modern terminals usually use electric RTGs, which are more environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, RMGs account for a high proportion of new large-scale specialized container terminals, while RTGs are widely used in small and medium-sized ports and multipurpose terminals. According to the statistics of China Communications and Transportation Association, in the construction of inland ports, RTG occupies 95% of the total number of yard bridges, but with the growth of automation demand and the improvement of environmental protection standards, “RMG will become the first choice of container terminal yard equipment supporting in the future”.
| Performance indicators | RMG cranes | RTG cranes | Advantages comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacidade nominal de elevação | 35-41 tons | 35-41 tons | / |
| Lifting speed (full load) | 13-20m/min | 10-18m/min | RMG 30% faster |
| Trolley speed | 70m/min or more | About 50m/min | RMG 40% faster |
| Stacking height | 5 - 6 layer | 4 - 5 layer | RMG more stable |
| Positioning accuracy | ±5mm | ±50mm | RMG 10 times more accurate |
| Service life | 25 years | 15 years | RMG 66% longer |
| Annual maintenance cost | 0.1% equipment value | 0.7% equipment value | RMG 7 times lower |
From the above comparative analysis of RTG and RMG Crane, we suggest that large automated terminals should give preference to RMG Crane, especially the dual cantilever design with an automated guided vehicle (AGV) solution. This combination has a high initial investment but low long-term operating costs and high throughput, making it suitable for large hub ports with stable cargo volumes. Small and medium-sized ports and multipurpose terminals are recommended to use RTG cranes with more flexibility in transshipment, such as electric RTG (E-RTG) or hybrid models.
Weihua is a well-known manufacturer of RTG and RMG cranes in China and can provide one-stop container handling solutions according to your needs. If you want to get more specific advice on RTG vs RMG selection, please contact our professional team.
Enviar pedido